Data Modeling
SQL vs NoSQL Database Differences
| SQL | NoSQL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| databases are primarily called as Relational Databases | database are primarily called as non-relational or distributed database | |||
| are table based databases | are document based, key-value pairs, graph databases or wide-column stores | |||
| have predefined schema | have dynamic schema | |||
| are vertically scalable | are horizontally scalable | |||
| are scaled by increasing he horse-power of the hardware | are scaled by increasing the databases servers in the pool ofresources to reduce load | |||
| databases uses SQL for defining and manipulating the data, which is very powerful | databases queries are focused on collection of documents | |||
| SQL databases are good fit for the complex query intensive environment | databases are not good fit for complex queries. On a high-level | |||
| SQL databases are vertically scalable. You can manage increasing load by increasing the CPU, RAM, SSD, etc, on a single server | NoSQL databases are horizontally scalable. You can just add few more servers easily in your NoSQL database infrastructure to handle the large traffic | ——————————————- | ————————————————- |
SQL Database Examples :
1-MySQL Community Edition 2-MS-SQL Server Express Edition 3-Oracle Express Edition
NoSQL Database Examples :
1- MongoDB 2-CouchDB 3-Redis
Data Modeling – Table Elements
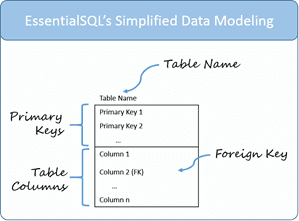
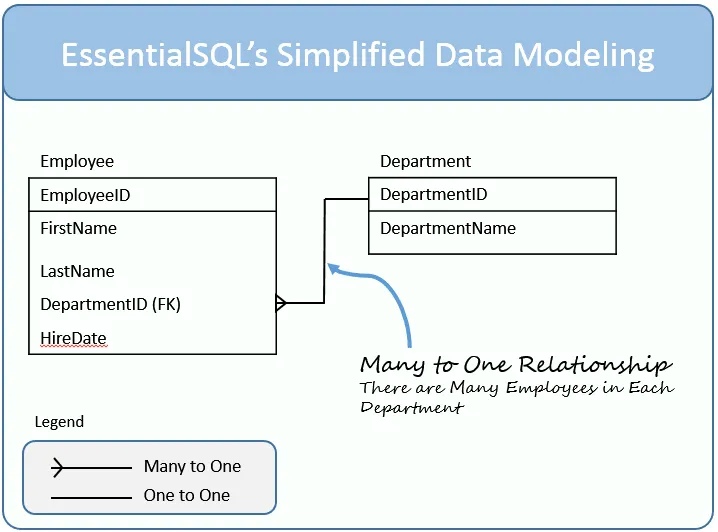
## Data Modeling – Table Relationships
Sequelize v6 :
Sequelize is a promise-based Node.js ORM tool for Postgres, MySQL, MariaDB, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server, Amazon Redshift and Snowflake’s Data Cloud. It features solid transaction support, relations, eager and lazy loading, read replication and more.
example
const { Sequelize, Model, DataTypes } = require('sequelize');
const sequelize = new Sequelize('sqlite::memory:');
class User extends Model {}
User.init({
username: DataTypes.STRING,
birthday: DataTypes.DATE
}, { sequelize, modelName: 'user' });
(async () => {
await sequelize.sync();
const jane = await User.create({
username: 'janedoe',
birthday: new Date(1980, 6, 20)
});
console.log(jane.toJSON());
})();